Primary Structure of Nucleic Acids. Describe the biochemical structure of ribonucleotides.
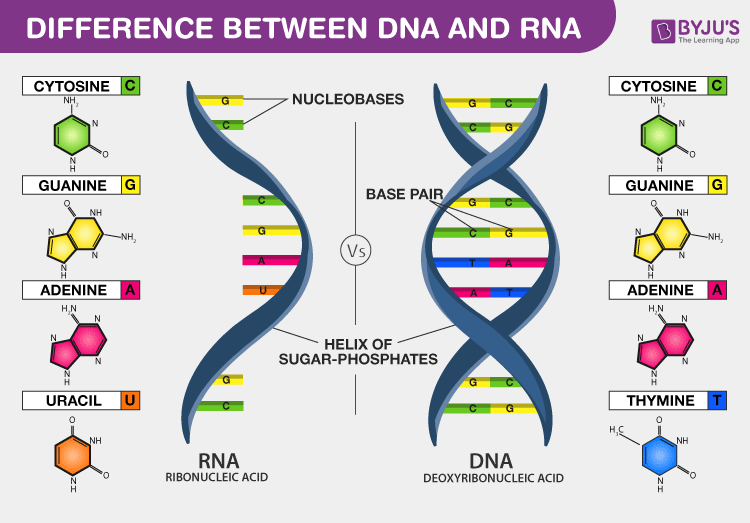
Dna Vs Rna Introduction And Differences Between Dna And Rna
DNA is the genetic material found in all living organisms ranging from single-celled bacteria to multicellular mammals.
. The books focus is on a survey of structures that are especially important for. Principles of Nucleic Acid Structure Second Edition provides the most complete and concise summary of underlying principles and approaches to studying nucleic acid structure including discussions of X-ray crystallography NMR molecular modelling and databases. Chemically speaking DNA and RNA are very similar.
A nucleotide is made up of three components. The backbone of the chain consists of. The five carbon sugar present in DNA is deoxyribose.
DNA and RNA are polynucleotides which contain a chain of nucleotides monomers with different nitrogenous bases. Is a chain of nucleotides covalently linked together. Describe the structures of nucleic acids 2.
DNA molecules are polymers and are made up of many smaller molecules called nucleotides. Each strand consists of alternating sugar and phosphates. A DNA molecule consists of two long polynucleotide chains composed of four types of nucleotide subunits.
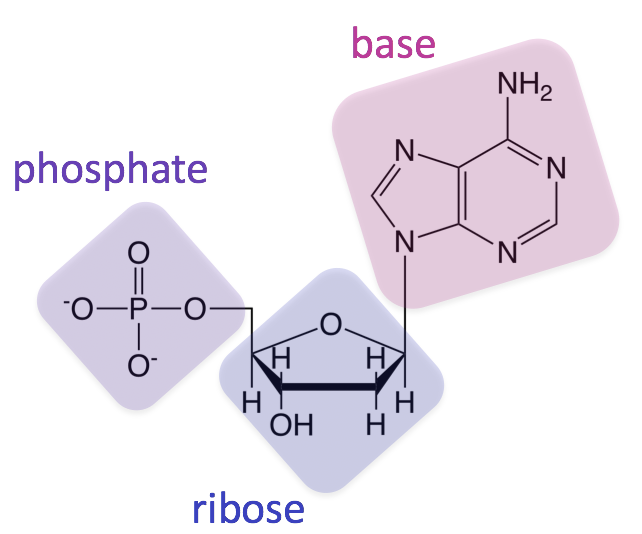
DNA is one of the two types of nucleic acids present in our bodies. A nucleotide is an organic molecule with a basic composition of a nitrogenous base pentose sugar and phosphate. Nucleotides are joined together through the phosphate group of one nucleotide connecting in an ester linkage to the OH group on the third carbon atom of the sugar unit of a second nucleotide.
Each nucleotide contains a phosphate group a sugar molecule and a nitrogenous base. They are long-chain polymers that consist of monomeric units called nucleotides. Science Biology QA Library Describe the structure of DNA.
You all are well versed in DNA and the function it performs. These vital macromolecules are typically made of oxygen nitrogen hydrogen phosphorus and most importantly carbon. Describe the structures of nucleic acids Get the answers you need now.
This unit joins to a third nucleotide and the process is repeated to produce a long nucleic acid chain Figure 195 Structure of a Segment of DNA. One to three phosphate groups a pentose sugar and a nitrogenous base. A DNA Molecule Consists of Two Complementary Chains of Nucleotides.
It is a nucleic. In the late nineteenth century a German biochemist found the nucleic acids long-chain polymers of nucleotides were. The building blocks of DNA are nucleotides which are made up of three parts.
A deoxyribose 5-carbon sugar a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. A nitrogenous base a pentose sugar and a phosphate group. DNA analysis can help build the family tree.
DNA is a double-stranded molecule organized into chromosome found in. During gene transcription a fragment of DNA called gene is used as template to create a complementary messenger RNA mRNA. It is therefore not surprising to see nucleic acids included in the compulsory core subject matter of all of the linear and modular A-.
In the area of genetic engineering and recombinant DNA technology which are covered in Booklet 7 of the BASC series have only been possible as a result of detailed understanding of the structure of DNA and RNA. The type of repeating monomer molecules in a DNA the three-dimensional structure of a DNA molecule the types of bonds that bond the monomers together in the backbone the types of bonds that bond the two nucleic acid strands together the types of bonds that hold the DNA into its three-dimensional structure. Nucleotides of Nucleic Acids.
Structurally each nucleotide is made up of a phosphate group a five-carbon sugar and a heterocyclic nitrogenous base A T C G and U. DNA is perhaps the most famous molecule on earth. The primary structure of the nucleic acid refers to the sequence of its nucleotide bases and the way these are covalently bonded to each other.
Transcription and translation are the two processes that convert a sequence of nucleotides from DNA into a sequence of amino acids to build the desired protein. Subsequently this mRNA is then used as template to generate a protein by a process called translation. Chemically speaking DNA and RNA are very similar.
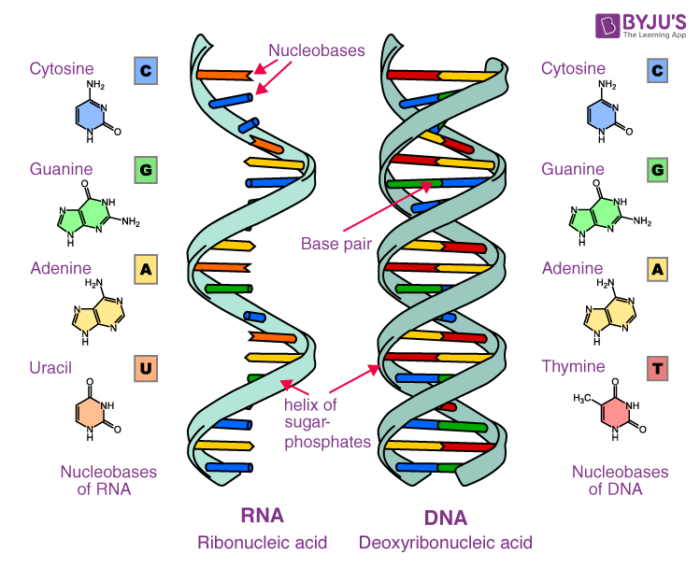
The two main types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid DNA and ribonucleic acid RNA. Nucleotides are joined together through the phosphate group of one nucleotide connecting in an ester linkage to the OH group on the third carbon atom of the sugar unit of a second nucleotide. Watson and Crick describe structure of DNA 1953 Photo.
Nucleic acid structure is often divided into four different levels. In fact you have probably even seen a diagram or picture of a DNA molecule. A C G T.
At physiological pH nucleic acids are negatively charged soluble in water form viscous solutions and are quite stable. Describe the similarities and differences between RNA and DNA. Littlelyna2love littlelyna2love 09252018 Biology High School answered PLEASE HELP.
The sequence of letters in a strand of DNA or RNA then is part of its primary structure. This structure is described as a double-helix as illustrated in the figure above. This mRNA is a single-stranded nucleic acid instead of a double-stranded nucleic acid like DNA.
There are two main types of nucleic acids. Nucleotides are essential for carrying out metabolic and physiological activities. Model of DNA molecule.
DNA molecules associate with proteins to form prokaryotic and eukaryotic chromosomes. DNA deoxyribonucleic acid molecules are nucleic acids which are the information-carrying molecules of the cell. The DNA structure can be thought of like a twisted ladder.
Here we explain what it is what it does its double helix structure and why it is so important to life. Each nucleotide comprises a phosphate group a 5-carbon sugar and a specific nitrogen base. DNA and RNA Comparison.
Primary secondary tertiary and. Now lets consider the structure of the two types of nucleic acids deoxyribonucleic acid DNA and ribonucleic acid RNA. Each of these chains is known as a DNA chain or a DNA strand.
There are four types of nitrogenous bases in DNA. It has a very distinct spiral shape. Made of two strands forming a double helix.
Two nucleic acid strands of either DNA or RNA can hydrogen bond together to form a double helix structure. Hydrogen bonds between the base portions of the nucleotides hold the two chains together. Nucleic acid structure refers to the structure of nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA.
In the complementary strand A is. DNA is composed of two sugar-phosphate backbones and nucleotide bases. Nucleic Acids - Structure and Function DNA and RNA in Cells.
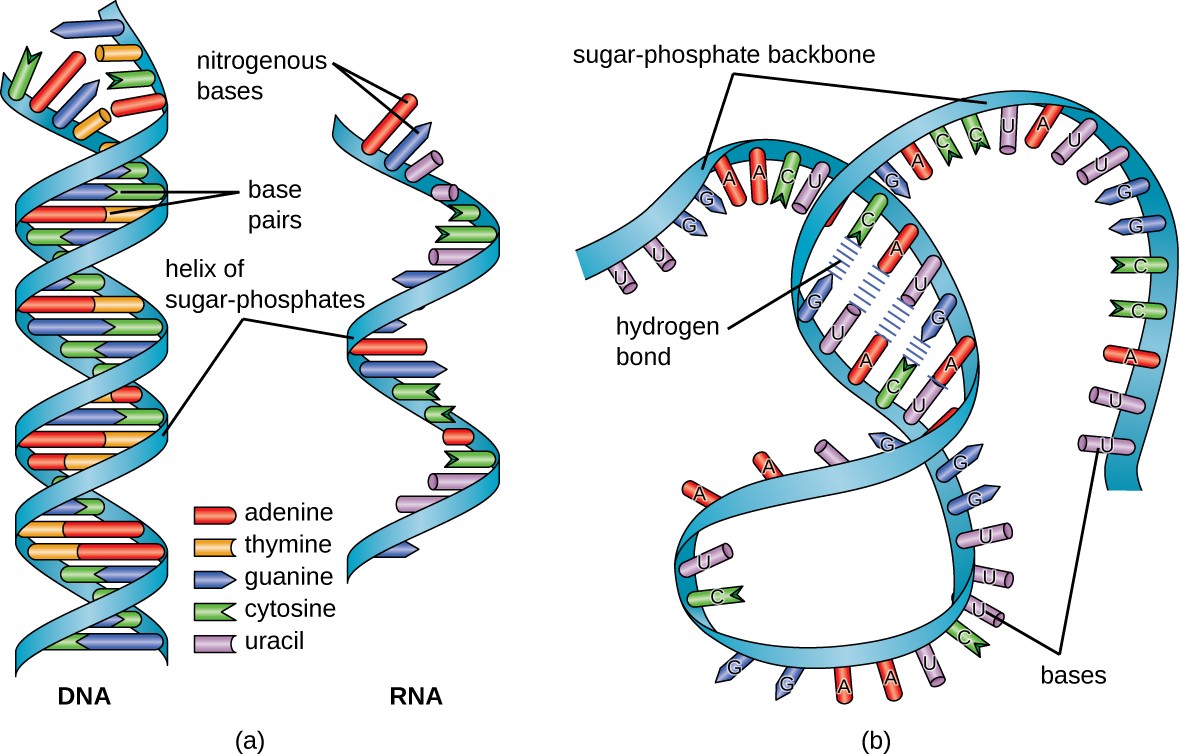
Structure And Function Of Rna Microbiology

Dna Vs Rna 5 Key Differences And Comparison Technology Networks
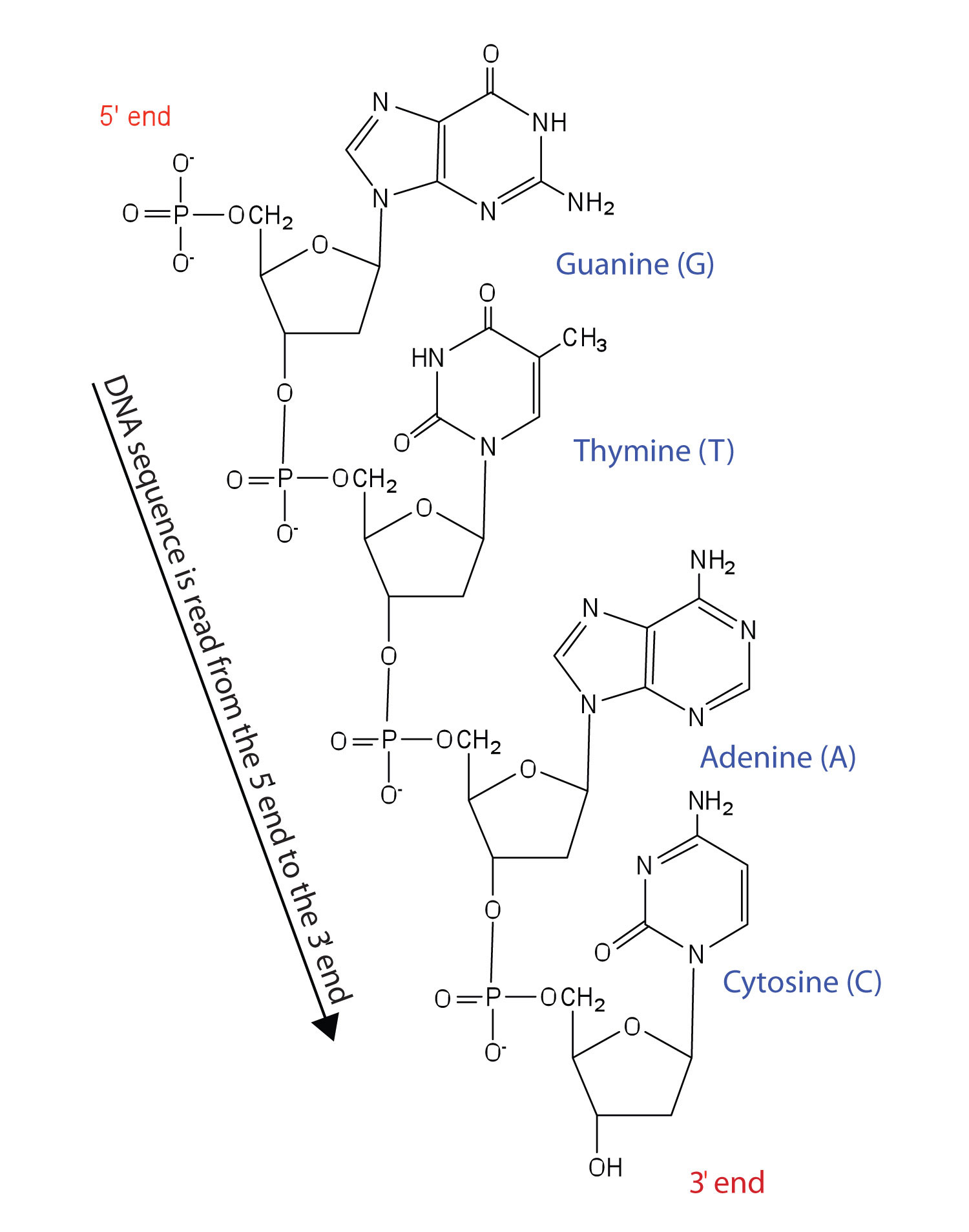
8 2 Nucleic Acid Structure Chemistry Libretexts
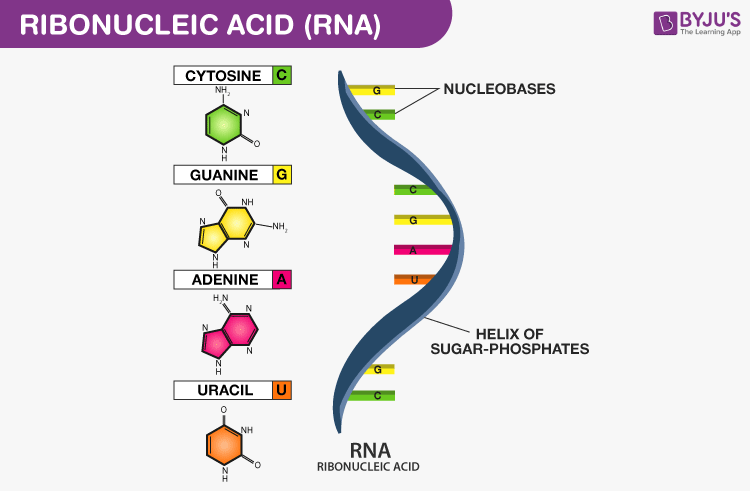
Rna Structure Functions And Types Of Rna

Nucleic Acids Definition Examples Functions Of Nucleic Acids

Nucleic Acid Types And Structure Biology Dictionary

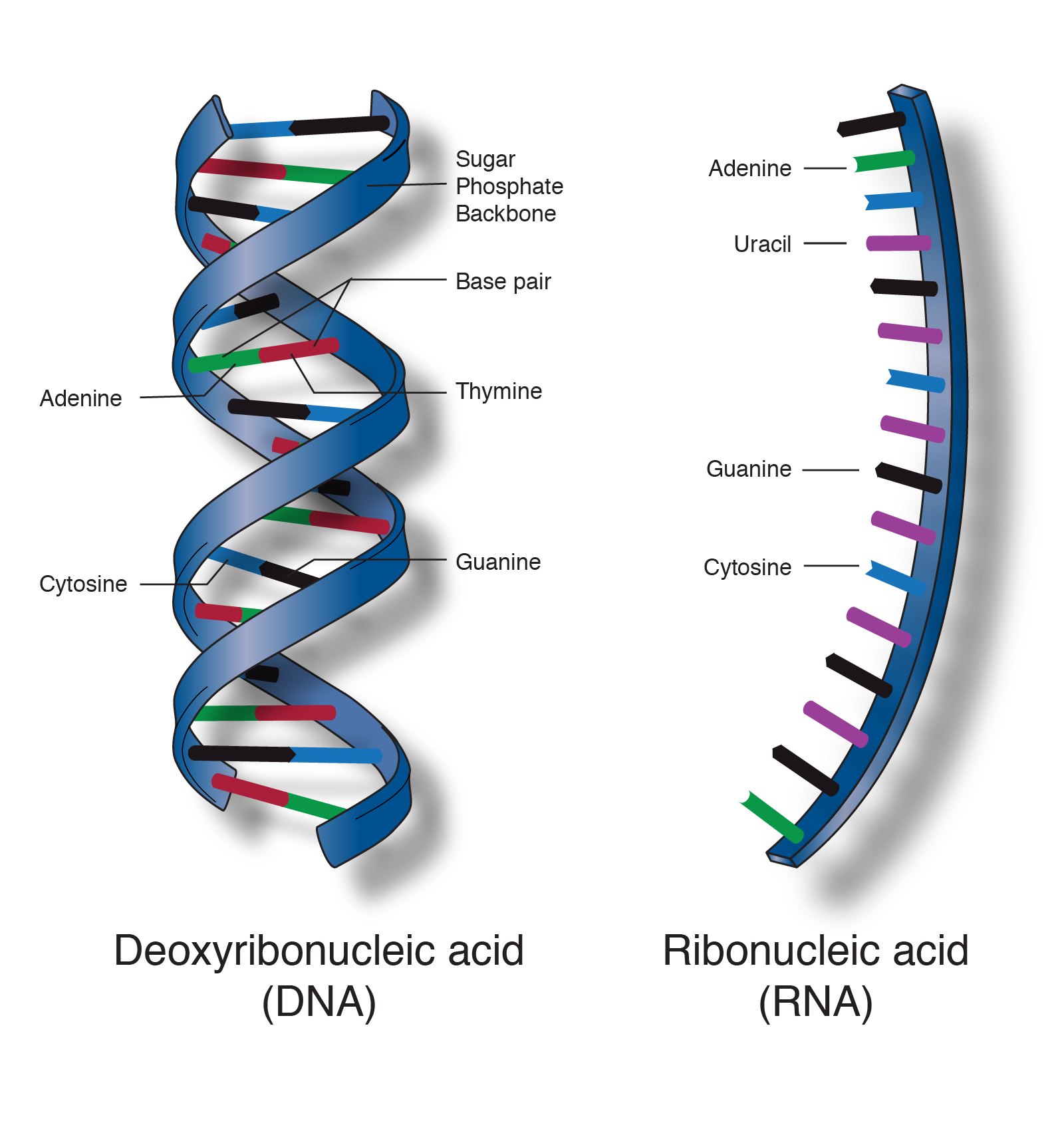
0 Comments